PPT Rotational and Angular Deformities in Children PowerPoint Presentation ID1010956
A comprehensive history and physical examination ( Table 1 3, 4 and Table 2 4 - 6 ) are often sufficient to differentiate normal variations in limb development from pathologic abnormalities,.

Internal Tibial Torsion Pediatrics Medbullets Step 1
Introduction Foot assessment is a common approach in clinical practice for classifying foot type with a view to identifying possible aetiological factors relating to injury and prescribing therapeutic interventions.

Normal Alignment of Lower Limb Axes and Orientation Bone and Spine
Torsional profile is a composite of measurements of the lower extremities. 6 It differentiates thigh, leg, and foot variations as the anatomic basis of a torsional abnormality. It also.

【医療職向け】足部評価leg heel angle(LHA)正常値・測り方は? 姿勢改善講座
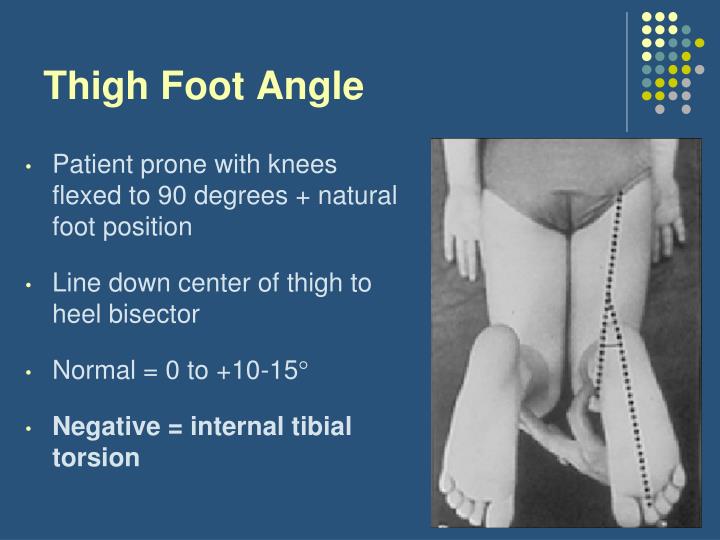
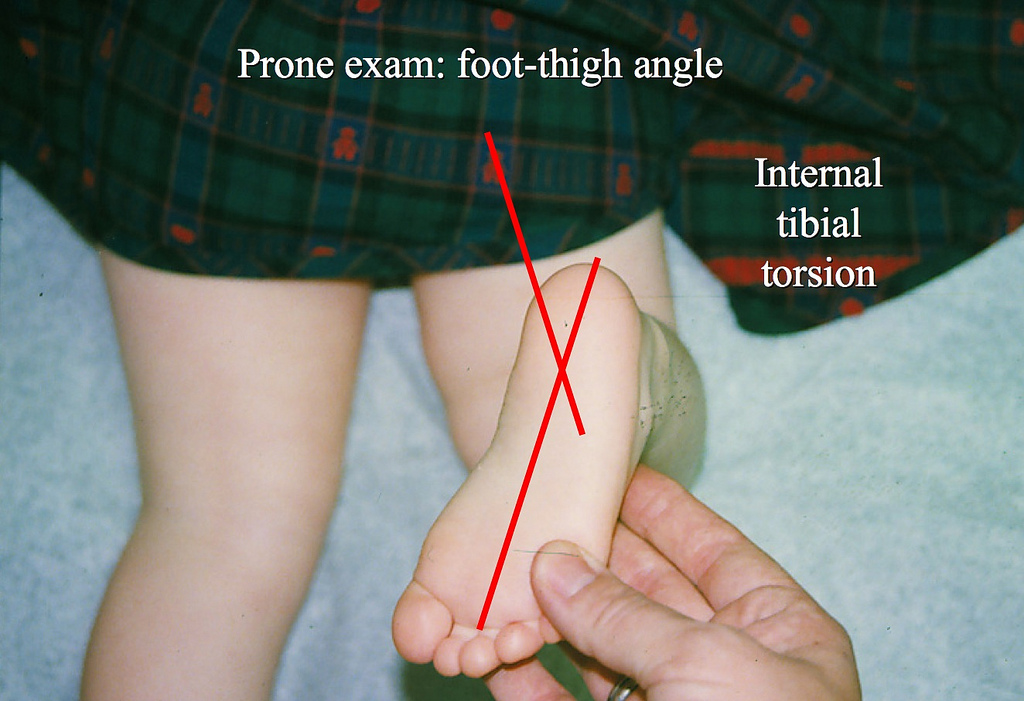
Measurement of photographic thigh-foot angle (P-TFA) and thigh-foot angle (TFA) using Thigh-Foot Supporter (TFS). Lying in the prone position keeping knee joint at 90°, the ankle joint in neutral, the sole of the foot in the parallel to the floor. Then we took photos to show both thighs and feet (A). TFA was measured fixing the tibia at 90.

Normal Foot and Ankle Radiographic Angles, Measurements, and Reference Points The Journal of
Anatomy The foot and ankle form a complex system which consists of 28 bones, 33 joints, 112 ligaments, controlled by 13 extrinsic and 21 intrinsic muscles. The foot is subdivided into the rearfoot, midfoot, and forefoot.

Definition of leg joint angles. a Modeled ankle joint position for the... Download Scientific
Causes of Foot Pain and Treatments. What You Should Know About Leg Pain. Natural Treatments for Plantar Fasciitis. Treating Achilles Tendinosis. An Overview of Shin Splints. Plantaris Muscle Pain: Strains and Tears at the Back of the Leg. Morton's Neuroma Foot Pain Symptoms and Treatment. Foot Problems and Deformities in Newborn Babies.

Hindfoot Alignment
Also known as "pigeon-toeing," this is caused by a rotational variation anywhere in the lower extremity that causes the foot to point inward. [1] [2] [3] [4] In coming to understand variational pathologies of the lower limb, it is important to be familiar with the normal growth and development of children's lower extremities.

The relationship between toeout angle during gait and progression of medial tibiofemoral
It is calculated by drawing a horizontal line at the distal end of the segment and measuring the angle from the right horizontal to the segment in a counterclockwise direction. Range of Motion
Internal Tibial Torsion Pediatrics Orthobullets
The foot progression angle represents the sum of tibial torsion, femoral torsion, and foot contour. This is the angle of the foot relative to a straight line being walked, with out-toeing receiving a positive value (Lincoln, 2003). Hip rotation should be measured with the patient prone in order to help stabilize the pelvis during the examination.

Normal Foot and Ankle Radiographic Angles, Measurements, and Reference Points The Journal of
Anatomic location may be bilateral but if unilateral most commonly involves the right lower extremity. Etiology Associated Conditions miserable malalignment syndrome a condition defined as external tibial torsion with femoral anteversion Osgood-Schlatter disease osteochondritis dessicans early degenerative joint disease

PPT Rotational and Angular Deformities in Children PowerPoint Presentation ID1010956
58 Bullets 83 Cards 2 Questions 6 Evidence 4 Video/Pods 2 Images summary Internal Tibial Torsion is a common condition in children less than age 4 which typically presents with internal rotation of the tibia and an in-toeing gait.

Effect of Patellar Displacement on Qangle Download Scientific Diagram
Anatomic location often bilateral be cautious of asymmetric abnormalities Etiology Femoral anteversion is characterized by increased anteversion of the femoral neck relative to the femur compensatory internal rotation of the femur lower extremity intoeing There are three main causes of intoeing including femoral anteversion (this topic)

Normal Foot and Ankle Radiographic Angles, Measurements, and Reference Points The Journal of
- thigh foot angle: - measured with the child in the prone position and knee flexed 90 deg, by observing the angle of the foot and the thigh; - thigh foot angle can upto - 5 deg (internal) in infants, but in young children the normal values is about 15 deg; - besides internal.

Thigh Knee Range of motion Joint, others, angle, foot, ankle png PNGWing
The goal of test is to inspect the external rotation (foot-thigh angle, best measured in a clinical setting )at the knee joint while the knees are in 30° and 90° of flexion. Patient in prone position: The clinician flexes the patient knees to 30° and places both hands on the feet of the patient, cupping his heels.

Illustration of clinical assessment of tibial torsion with the... Download Scientific Diagram
Thigh-foot angle (TFa) Thigh-foot angle (TFa) 1,679 views A useful clinical tool for in-toe or out-toe gaits, the TFa avails distinction between femoral/tibial components, genicular position, tibial torsion. View Resource

Definitions of the thigh, knee joint, and ankle joint angles Download Scientific Diagram
Tibial torsion Tibial torsion is inward twisting of the tibia (shinbone) and is the most common cause of intoeing.
